K-casein B
k-casein and Cheese
|
 |
|||
|
“K-casein B milk incorporates a higher amount of fat and protein
into cheese.”
“Curds form k-casein milk show a better elasticity and are more
suitable to syneresis, while the curd form K-casein A milk gives
less firm curds.”
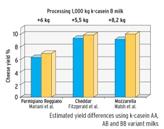
“Compared to k-casein A, k-casein B gives the milk better cheesemaking
properties: a shorter rennet coagulation time and firmer
curds and for certain types of cheese, a higher cheese yielding ability
(the difference between the two milks ranges from 4% to 8%).”
“It is estimated that the actual yield of cheese in a plant producing
20,000 tonnes per year from k-casein AA milk would increase
to approximately 21,180 tonnes of Cheddar, or 21,780 tonnes of
Mozzarella if made from k-casein BB milk.”
“The yield of Parmigiano Reggiano increases of +6 kg per cauldron if only k-casein milk is processed compared to the yield of Parmigiano Reggiano from only k-casein AA milk.”
“K-casein BB milk coagulates better compared to k-casein AA
or AB milk.”
“Milk with a higher K-casein B content has also higher casein,
calcium and phosphorus contents .”
|
||||
Identification Number
00247400237


 Download
Download