|
Milk caseins are modified proteins by post translational modifications (phosphorylation and glycosylation). As the higher number of proline residues, which prevent the formation of highly ordered secondary structures, and the lack of disulphide bonds, the conformation of caseins was historically compared to random-coil proteins.
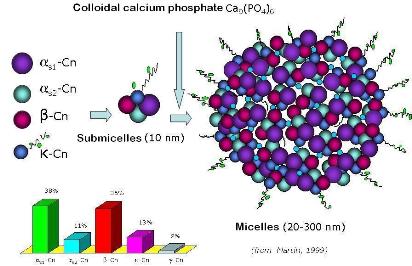
In milk, caseins form large colloidal particles, spherical in shape, named casein micelles. Besides caseins, micelle includes low molecular mass particles referred as colloidal calcium phosphate (CCP). Caseins interact by means of secondary hydrophobic bond and form salt bridges with CCP.
K-casein: due to its amphiphilic structure, k-casein is mainly located on the surface of the micelle. In particular, the hydrophilic C-terminal region protrudes from the surface (hairy layer) and it is responsible for micelle stability. In fact, the removing of the hairy layer by hydrolysis (rennet coagulation) lead to destabilisation (precipitation) of casein
|